1. Understanding Testosterone in Men
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone, produced primarily in the testes and regulated by the brain’s pituitary gland.
It plays a crucial role in:
Male puberty and sexual development
Muscle and bone strength
Red blood cell production
Libido (sex drive)
Mood and mental clarity
When testosterone levels drop below the normal range, it can result in low testosterone, also known as male hypogonadism.
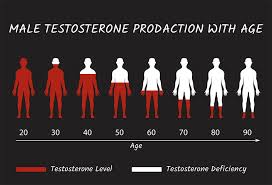
2. What is Hormonal Imbalance in Men?
Hormonal imbalance means one or more hormones in the body are too high or too low, disrupting normal function.
In men, the main hormonal imbalances involve:
Low testosterone (T)
High estrogen
Thyroid dysfunction (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism)
Elevated cortisol (stress hormone)
Insulin resistance
These hormones interact with each other. When testosterone drops, it can lead to emotional, physical, and sexual health problems.
3. Causes of Low Testosterone in Men
Aging – Testosterone naturally decreases after age 30.
Obesity – Fat cells convert testosterone into estrogen.
Chronic stress – Raises cortisol, which suppresses testosterone.
Lack of sleep – Reduces testosterone production.
Poor diet – High sugar, low protein, and nutrient deficiencies.
Sedentary lifestyle – Lowers natural testosterone output.
Environmental toxins – Plastics, pesticides, and BPA mimic estrogen.
Medications – Steroids, opioids, antidepressants.
Medical conditions – Diabetes, testicular injury, liver/kidney disease.
4. Symptoms of Low Testosterone in Men
Low testosterone affects multiple systems. Symptoms include:
🔸 Physical Symptoms:
Decreased muscle mass and strength
Increased belly fat
Fatigue and low energy
Reduced stamina
Decreased facial/body hair
Gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue)
🔸 Sexual Symptoms:
Low sex drive (libido)
Difficulty achieving or maintaining erections
Reduced semen volume
Infertility
🔸 Mental & Emotional Symptoms:
Depression or mood swings
Poor concentration and memory
Low confidence or motivation
Irritability and anxiety
5. How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosing low testosterone and hormonal imbalance involves:
Blood Tests:
Total testosterone
Free testosterone (active form)
LH (Luteinizing Hormone) & FSH (pituitary hormones)
Prolactin (to check pituitary gland function)
Estradiol (estrogen levels in men)
Cortisol and thyroid hormone (T3, T4, TSH)
Insulin and fasting glucose
Symptom Evaluation:
Doctors assess symptoms, medical history, sleep habits, stress levels, and lifestyle factors.
6. Treatment Options for Men
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the imbalance:
🔸 Lifestyle Changes:
Exercise – Especially resistance and weight training.
Healthy diet – High in protein, healthy fats, zinc, and vitamin D.
Weight loss – Reduces estrogen and increases testosterone.
Better sleep – Aim for 7–9 hours per night.
Stress management – Meditation, yoga, therapy.
🔸 Medical Treatments:
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) – Includes injections, gels, patches, or pellets.
Clomiphene citrate – Helps stimulate natural testosterone production (used in younger men).
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) – Preserves fertility while boosting testosterone.
Treatment of other imbalances – Thyroid medication, insulin regulation, etc.
⚠️ Note: Hormone therapy must be prescribed and monitored by a doctor to avoid serious side effects like infertility, heart risk, or prostate issues.
7. Risks of Untreated Low Testosterone
Muscle wasting and weight gain
Bone density loss (osteoporosis)
Erectile dysfunction and infertility
Chronic fatigue and depression
Cognitive decline
Relationship issues and poor quality of life
🩺 Realistic Doctor-to-Doctor Conversation: Male Hormonal Imbalance
Dr. Ayesha Malik – Endocrinologist
Dr. Imran Qureshi – Urologist
Dr. Malik:
“Male patients with hormonal issues are often misdiagnosed. Many think fatigue or low sex drive is just part of aging. But when we test, we find testosterone levels far below normal—even in men under 40.”
Dr. Qureshi:
“Absolutely. I’ve had patients in their 30s suffering from erectile dysfunction. They assume it’s stress or anxiety, but in many cases, it’s hormonal—especially low testosterone or thyroid dysfunction.”
Dr. Malik:
“And it’s not just testosterone. We often see elevated estrogen, high cortisol, or insulin resistance, all of which disrupt male health. These hormones work together like a symphony—when one is out of tune, everything is affected.”
Dr. Qureshi:
“What’s your protocol for treatment?”
Dr. Malik:
“First, lifestyle—clean up the diet, manage stress, prioritize sleep, and encourage regular exercise. If levels remain low and symptoms persist, then I recommend hormone therapy, but only after full lab work and discussion of fertility.”
Dr. Qureshi:
“Yes, TRT can reduce sperm production. In younger men, I usually go for clomiphene or hCG instead of direct testosterone to preserve fertility.”
Dr. Malik:
“Exactly. And people often don’t realize how dangerous it is to use online testosterone boosters or steroids without supervision. It can lead to heart problems, mood swings, and permanent hormone suppression.”
